Multi-Electrode Arrays Processing¶
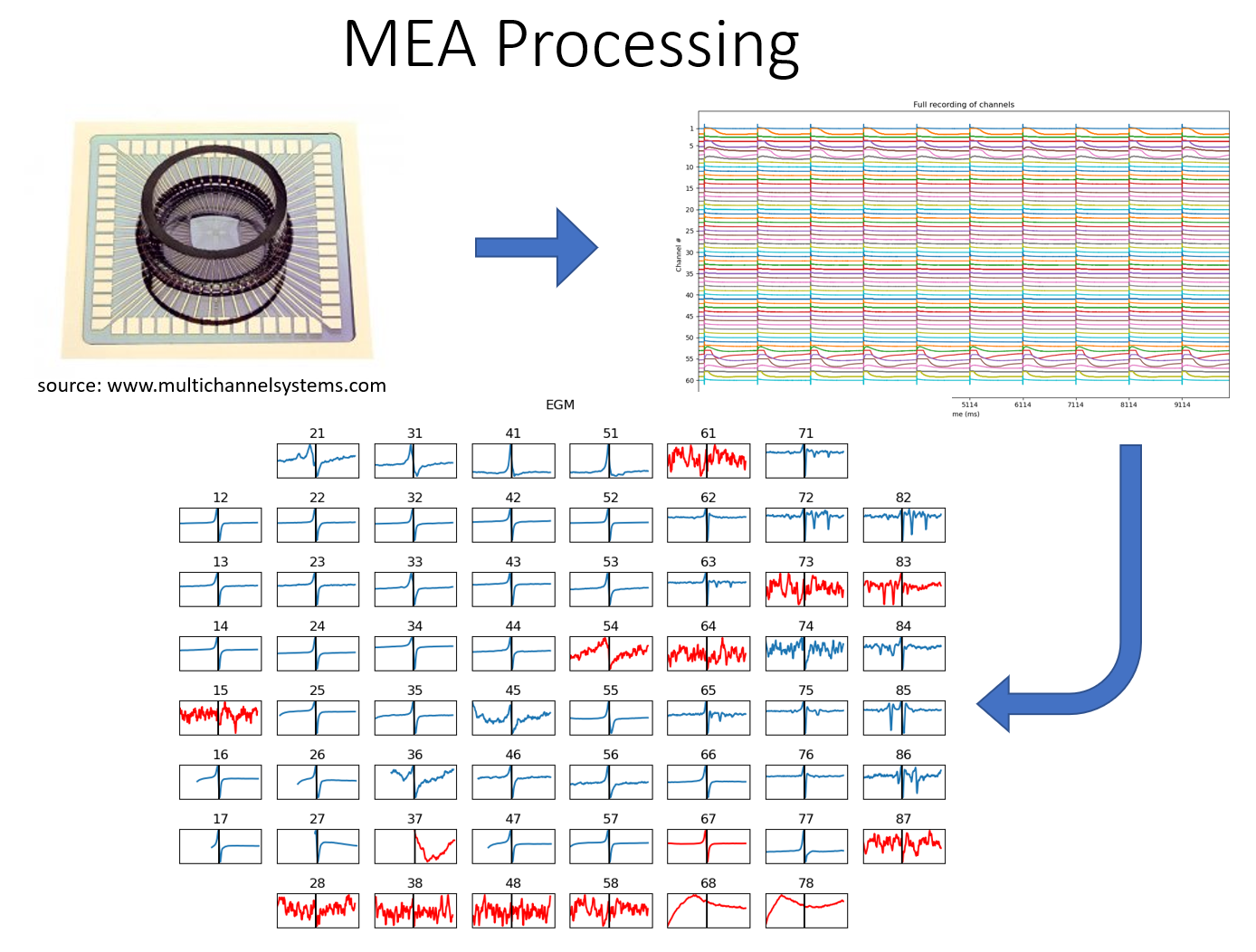
Backgorund¶
#TODO
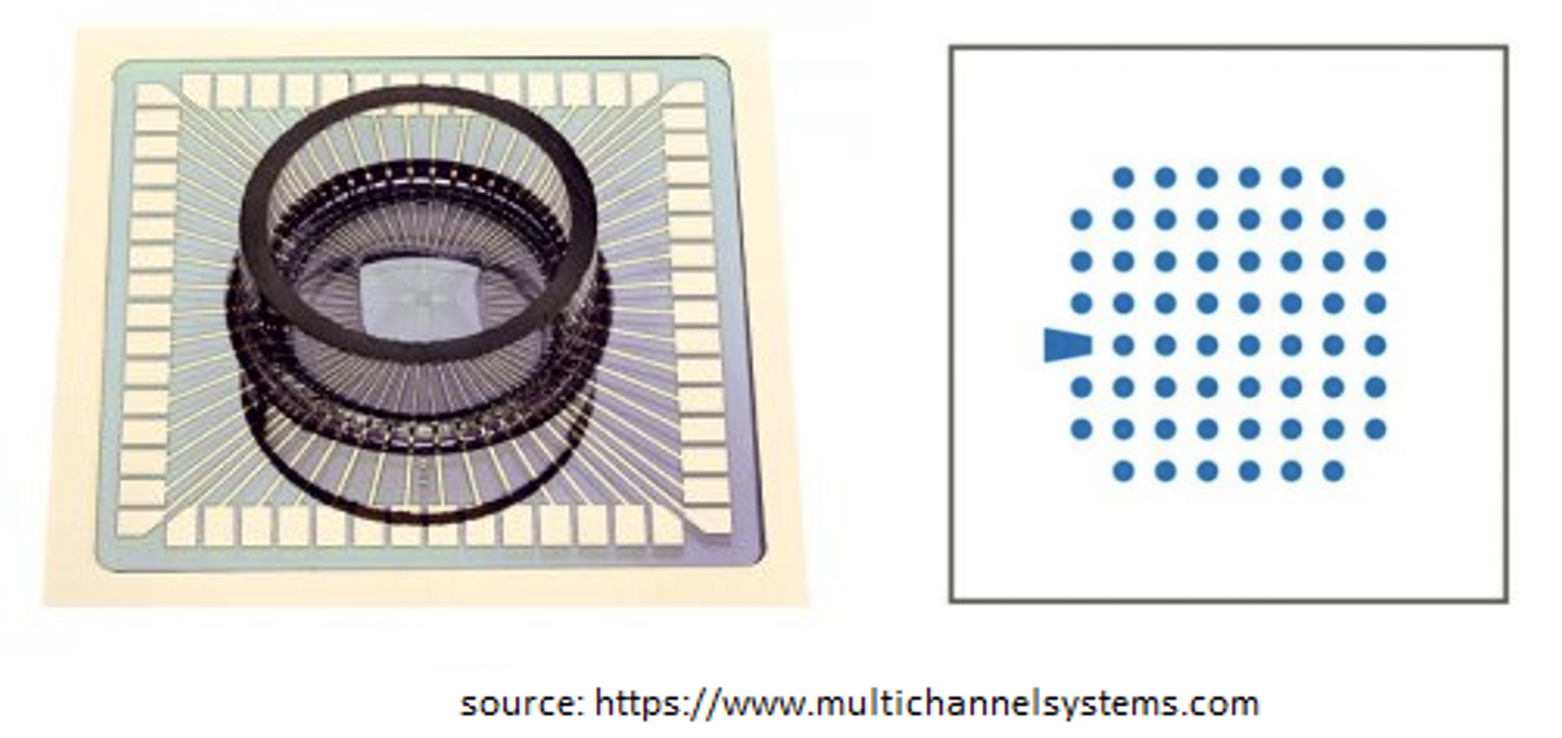
Multi-Electrode Arrays System utilies an array of electrodes mounted on a small plate as a grid electrodes (e.g. 60) evenly spaced (700mm apart). It is used to analyse the eletrophysiology of cells/tissues under different clinical conditions by stimulating with certain voltage on a regular intervals. As shown in figure below, a plate of MEA system of 60 electrodes (source: https://www.multichannelsystems.com/products/meas-60-electrodes). One of the commonly used research field is the cardiac electrophysiology.
This python library analyse the recorded signal file, by extracting the electrograms (EGMs) from signal recoding of each eletrodes, and extracting the features of each EGM.
#TODO
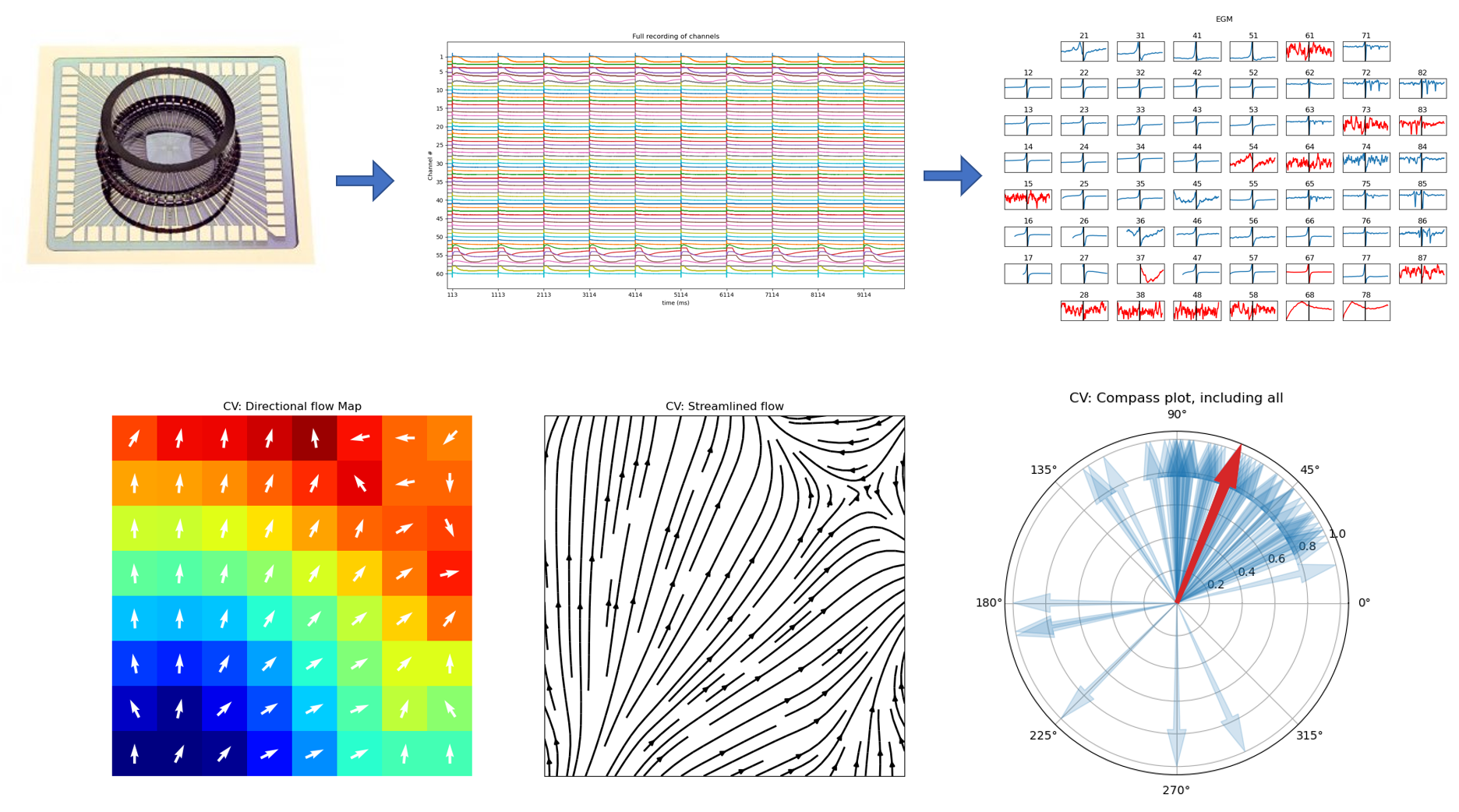
Complete Analysis of a recording¶
#TODO
One of the simple function to provide complete analysis of recorded file is to use `spkit.mea.analyse_mea_file` function.
This uses the default settings of all the paramters for extracting electrograms, identifying bad eletrodes, extracting features and plotting figures.
`spkit.mea.analyse_mea_file` needs two essential inputs, `files_name` : a full path of recoding file in ‘.h5’ format and `stim_fhz` frequency of stimulus in Hz.
import spkit as sp
sp.mea.analyse_mea_file(files_name,stim_fhz=1)

Step-wise Analysis¶
#TODO
There are 13 steps to analyse a recording file, which are as follow
Read HDF File
Stim loc
Align Cycles
Average Cycles/Select one
Activation Time
Activation & Repolarisation Time
APD
Extract EGM
EGM Feature Extraction
BAD Channels
Feature Matrix
Interpolation
Conduction Velocity
1. Read HDF File¶
#TODO
sp.io.read_hdf
2. Stim Localisation¶
#TODO
sp.mea.get_stim_loc
3. Alignment of Stim Cycles¶
#TODO
sp.mea.align_cycles
4. Averaging Cycles or Selecting one¶
#TODO
5. Activation Time¶
#TODO
sp.mea.activation_time_loc
6. Repolarisation Time (optional)¶
#TODO
sp.mea.activation_repol_time_loc
7. APD (if RT is computed)¶
#TODO
apd_ms = rt_loc_ms-at_loc_ms
8. Extracting EGM¶
#TODO
sp.mea.extract_egm
9. EGM Feature Extraction¶
#TODO
sp.mea.egm_features
10. Identifying BAD Channels/electrodes¶
#TODO
sp.mea.find_bad_channels_idx
11. Creating Feature Matrix¶
#TODO
sp.mea.feature_mat
12. Interpolation¶
#TODO
sp.fill_nans_2d
13. Conduction Velocity¶
#TODO
sp.mea.compute_cv
Plots and Figures¶
#TODO
sp.mea.plot_mea_grid
sp.mea.mea_feature_map
sp.mea.mat_list_show
sp.direction_flow_map
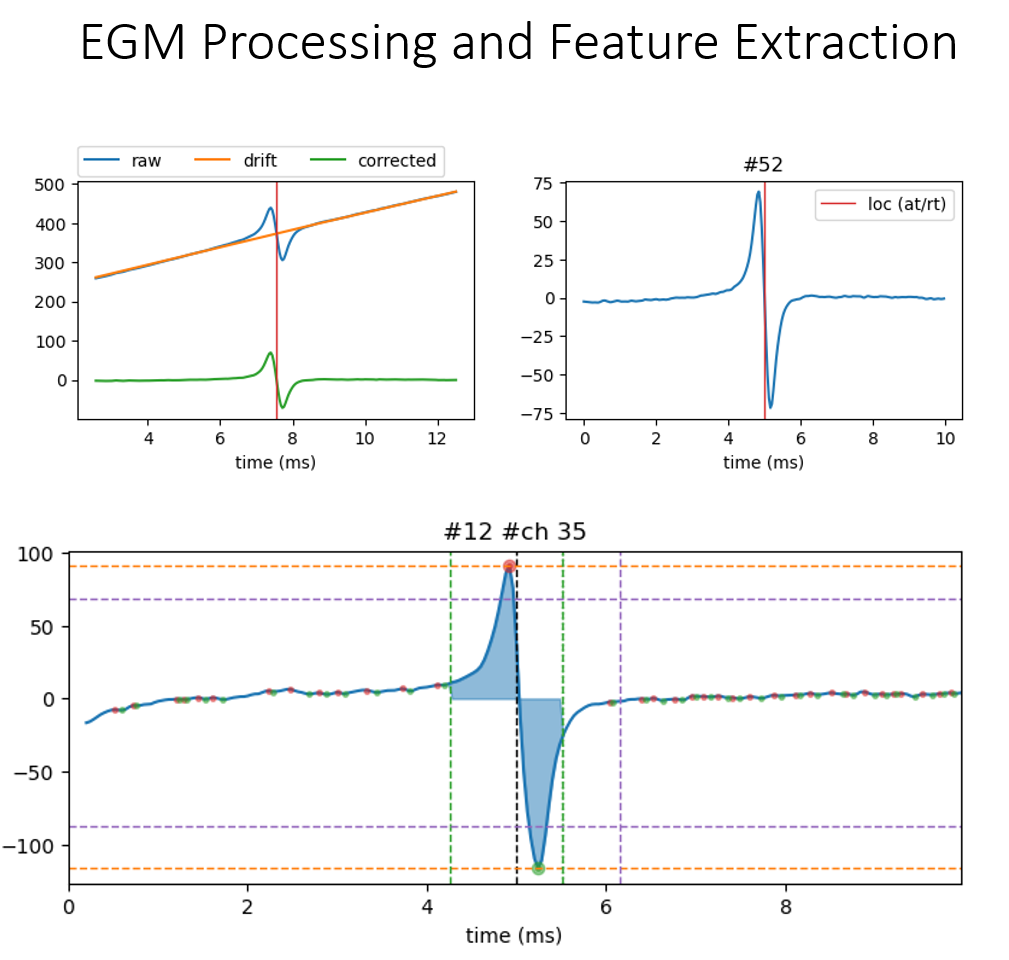
Extracting EGM¶
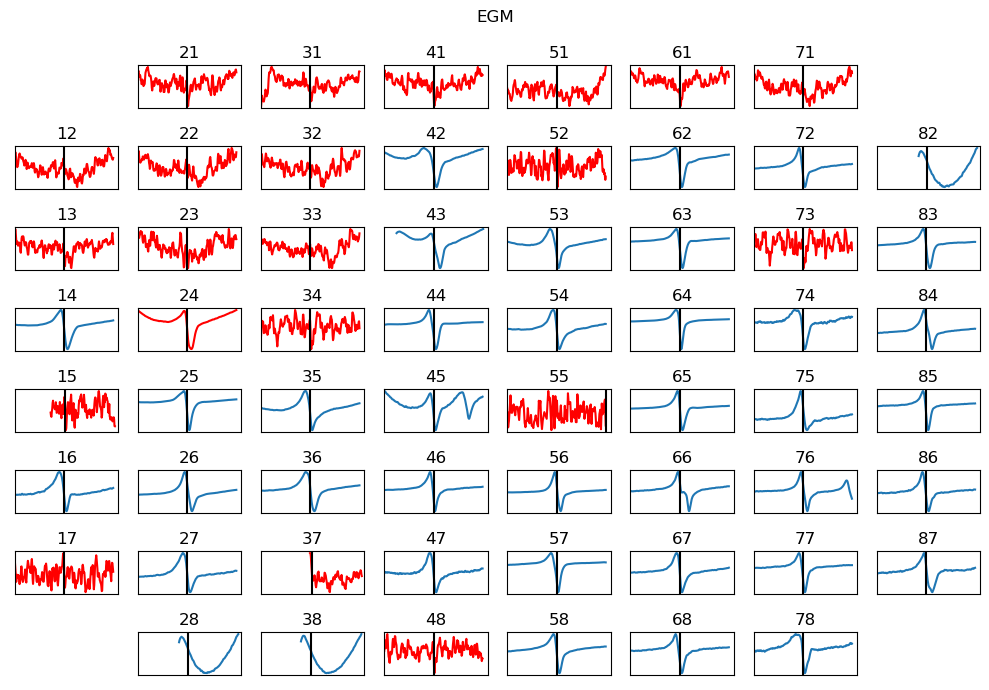
EGM Processing & Feature Extractions¶
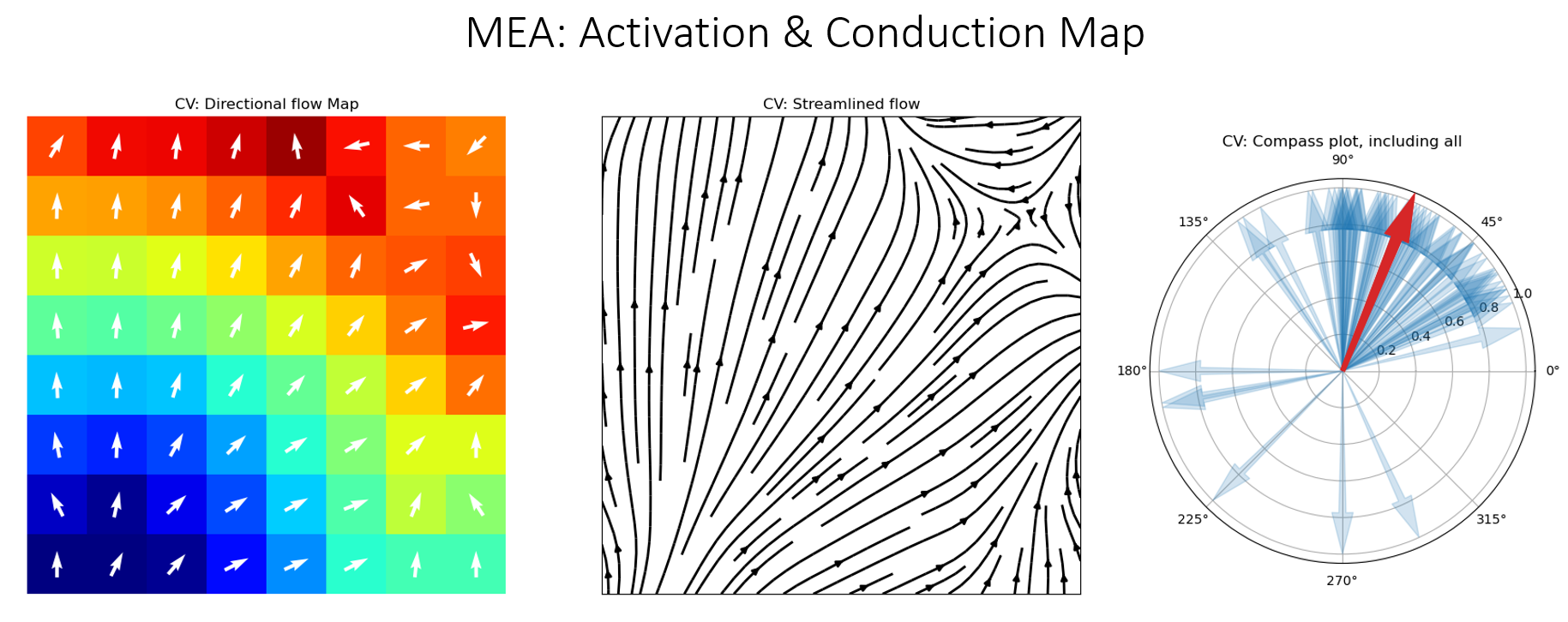
Conduction and Activation Map¶
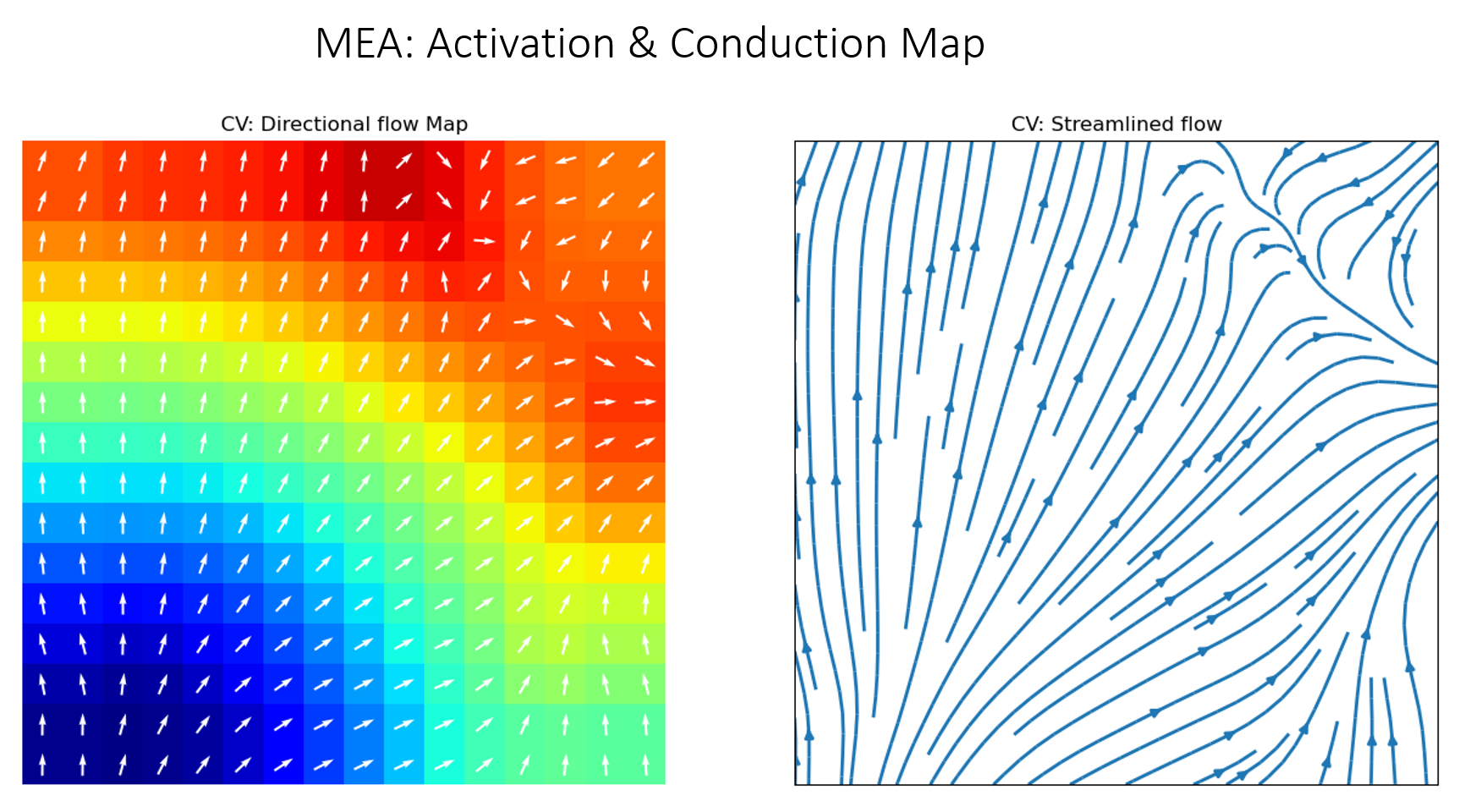
#TODO